How to Check Ethernet Connection Speed in Mac - Leisure fantastic wireless network is a sure thing you desire, but not comparable to the solidity and reliability of a wired network connection.
From where you can find out if your ethernet connection running at 10, 100 or 1000 Mbit/s? This article will tell you where I check the connection speed on Mac.
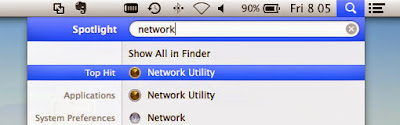
2. Next, open the Network Utility on your Mac. It is located in the Applications> Utilities> Network Utility. Or, find Network Utility in Spotlight Search.
3. On the Info tab, under Network Interface, use the drop-down menu to select Ethernet.
4. Then you will see the details of network connections including network address and connection speed.
Done! Now that you know how to determine the speed of your ethernet connection. You are currently still in the Network Utility? You can check out the other useful features of the Network Utility in other tabs, as shown below.
From where you can find out if your ethernet connection running at 10, 100 or 1000 Mbit/s? This article will tell you where I check the connection speed on Mac.
How to Check Ethernet Connection Speed in Mac
1. Make sure your ethernet cable is plugged in and to make sure that you are connected to the network, open System Preferences> Network.2. Next, open the Network Utility on your Mac. It is located in the Applications> Utilities> Network Utility. Or, find Network Utility in Spotlight Search.
3. On the Info tab, under Network Interface, use the drop-down menu to select Ethernet.
4. Then you will see the details of network connections including network address and connection speed.
Done! Now that you know how to determine the speed of your ethernet connection. You are currently still in the Network Utility? You can check out the other useful features of the Network Utility in other tabs, as shown below.
- Ping: Allows you to test how long it takes to send messages to the remote server and receive a response. Size in milliseconds.
- Whois: Find out who the owner of the registered domain name.
- Traceroute: Navigate your request physical path along the Internet when you connect to the remote server.